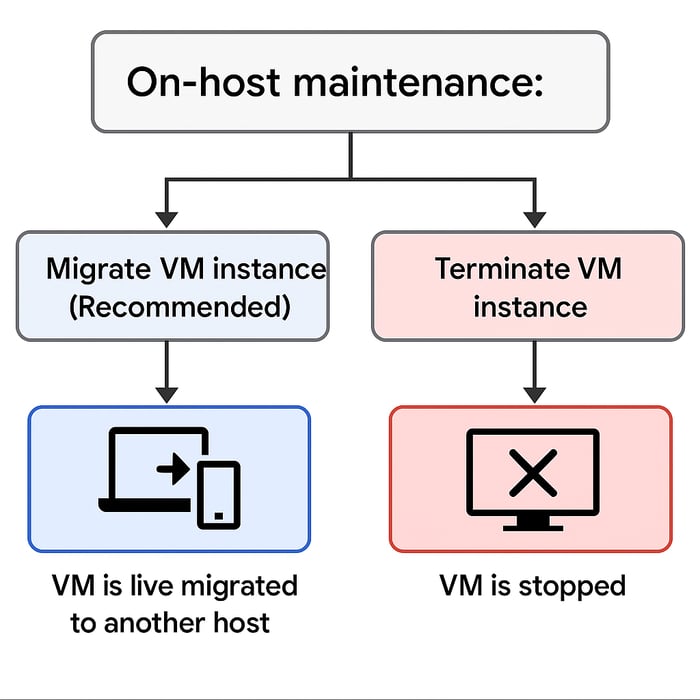
In the world of cloud computing, the seamless operation of virtual machines (VMs) is paramount. However, underlying this virtual layer is a vast physical infrastructure of servers, networking gear, and power systems that, like any complex machinery, requires periodic maintenance and updates. This essential upkeep ensures the long-term health, security, and performance of the cloud platform. Google Cloud is no exception. The critical question for users of Google Compute Engine then becomes: how does this necessary physical maintenance impact the virtual instances running their vital workloads? The answer lies in a thoughtfully designed feature highlighted by the "On-host maintenance" parameter.
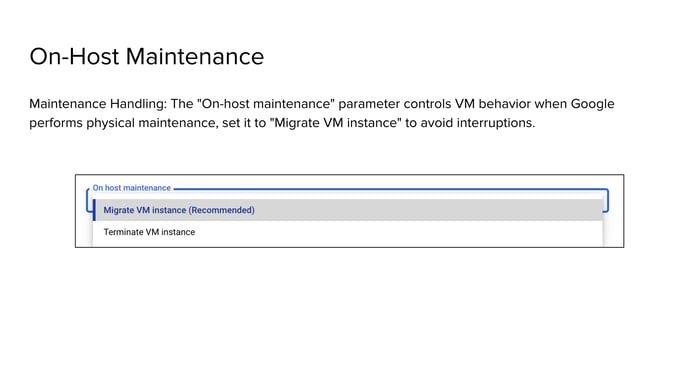
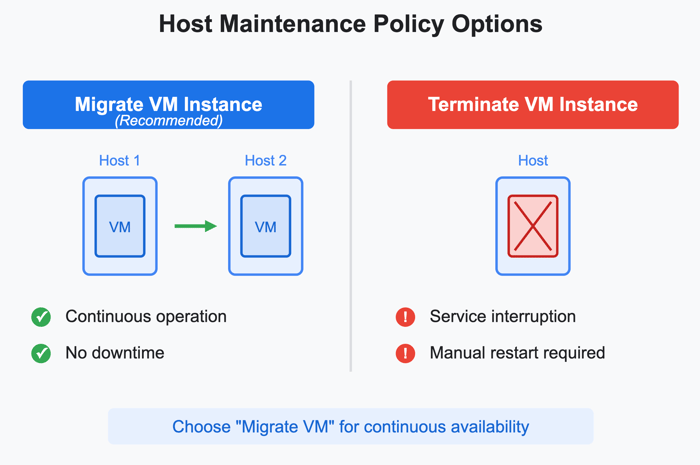
This specific setting, as depicted in the configuration options, directly governs the behavior of a VM instance when Google needs to perform maintenance on the physical host server supporting that VM. The image clearly presents two fundamental choices, each with distinct consequences for your running applications: "Migrate VM instance (Recommended)" and "Terminate VM instance."
Terminate VM Instance
Let's first consider the "Terminate VM instance" option. Selecting this means that when the underlying host requires maintenance, your VM will be shut down. This approach, while straightforward, introduces a period of unavailability for any services or applications hosted on that instance. For applications that are not designed for fault tolerance or that cannot sustain downtime, this option could lead to service interruptions, potential data loss if states are not properly saved, and require manual intervention to restart services post-maintenance. While there might be extremely specific scenarios, such as short-lived, non-critical batch processing jobs designed to be ephemeral, where termination is acceptable, it is generally a path that compromises continuous availability.
Migrate VM Instance
In stark contrast, the "Migrate VM instance" option, prominently marked as "Recommended," offers a far more robust and business-friendly solution. This setting leverages Google Cloud's sophisticated live migration technology. When maintenance is scheduled for a host, Google's infrastructure automatically moves your running VM. This includes its memory, CPU state, and network connections. The VM is moved to a different, healthy host server within the same zone. This process is engineered to be largely transparent to the VM and its running applications, typically occurring with a freeze time measured in milliseconds or, at most, a few seconds. The end-user experience, and indeed the application itself, ideally perceives no interruption.
The "Recommended" label is not arbitrary. It reflects a commitment to uptime and operational continuity. By choosing migration, businesses can effectively decouple their virtual workloads from the physical maintenance cycles of the underlying hardware. This proactive approach ensures that necessary infrastructure enhancements and security patches can be applied by Google without causing detrimental downtime for customer applications. It allows organizations to meet their service level objectives (SLOs) and maintain business continuity, focusing on their application logic rather than the intricacies of physical server management.
Summary
Ultimately, the "On-host maintenance" setting reflects Google Cloud's engineering approach. It gives users a choice based on their specific availability needs. For most workloads, the live migration option simply makes practical sense, helping Google Compute Engine instances continue running during infrastructure updates. This capability contributes to the reliability of cloud applications.
Learn More
On-host maintenance in Compute Engine is explored, along with many other topics, as part of my Professional Cloud Architect and Associate Cloud Engineer courses.